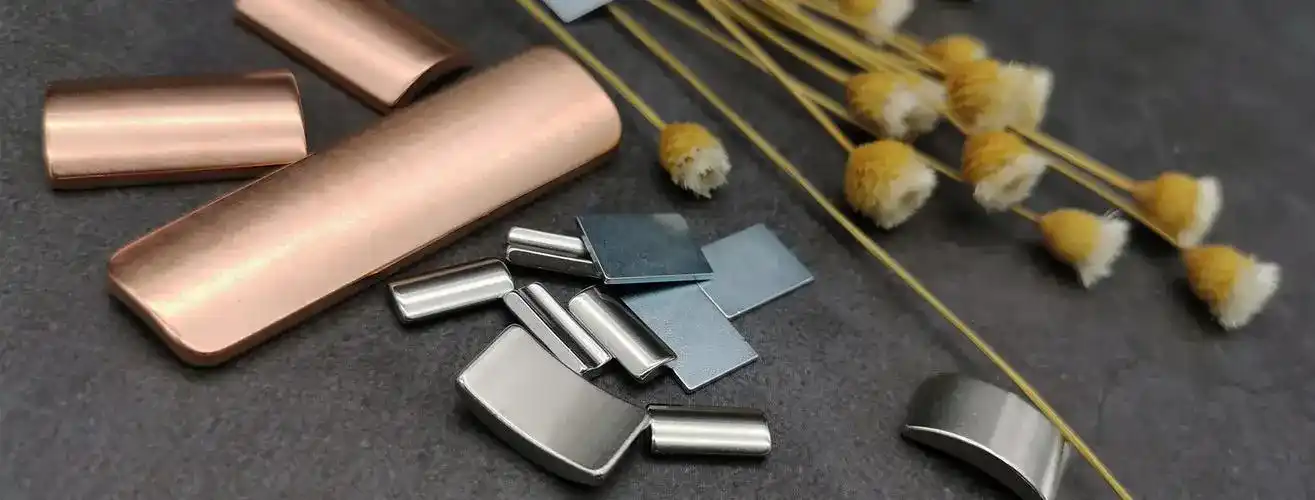
Neodymium magnets are also called NdFeB magnets. Neodymium magnets are permanent magnets made of alloys of neodymium, iron, and boron. They are substances with the largest magnetic energy product in the world. Before understanding neodymium magnets, we first understand what are rare earths.
Table of Contents
what are rare earths?
Rare earth is a general term for seventeen metal elements including lanthanides, scandium and yttrium in the chemical periodic table.
There are 250 kinds of rare earth ores in nature.Rare earths have been discovered since the end of the 18th century.
At that time, people often referred to solid oxides insoluble in water as soil. For example, aluminum oxide was called clay, and calcium oxide was called alkaline earth.

Overview of Rare Earths in China
1: China’s rare earth reserves rank among the highest in the world. In the case of the world’s total rare earth resources of 130 million tons, my country accounts for 44 million tons,
accounting for one-third of the world’s total rare earth resources. Therefore, there is a saying that “the Middle East has oil, and China has rare earth”
2: China’s rare earth smelting capacity is first-class in the world, accounting for 88% of the world’s rare earth smelting, and the world takes China’s smelting technology as the standard
3: China is a major exporter of rare earth. Japan, the United States, the Netherlands, South Korea, Italy,
and other countries are all trading partners of Chinese rare earth products and have exported rare earth and rare earth products to more than 60 countries and regions.
Many countries in the world rely on my country’s rare earth resources, and their advantages in reserves, production, and export trade have allowed China to once occupy a monopoly position in rare earth resources.
What is neodymium magnet?
Neodymium magnet is a type of rare earth magnet that is widely considered to be the strongest and most powerful permanent magnet available today. It is made of a combination of neodymium, iron, and boron (NdFeB), which are all rare earth elements.
Neodymium magnets are the strongest type of permanent magnet available, with a high magnetic field strength and excellent magnetic properties. They are used in a wide range of applications, including electric motors, generators, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, and computer hard drives.
Neodymium magnets are known for their high magnetic strength and excellent performance in applications where size and weight are critical factors. They are capable of producing magnetic fields that are significantly stronger than other types of magnets, which makes them ideal for use in many industrial and scientific applications.
Characteristics of neodymium magnets?
Neodymium magnet grade
The grades of NdFeB magnets are divided into N35, N38, N42, N38SH, etc. The classification of these grades is based on the grade of NdFeB materials. Generally speaking,
the higher the number (the number after N), the stronger the magnet will be. The highest grade of NdFeB magnets currently available is N52. Those letters following the grade refer to the temperature grade of the magnet. If there are no letters following the grade, then the magnet is standard temperature neodymium. The temperature ratings are standard (no designation) – M – H – SH – UH – EH.
| Material | Remanence(Br) | Coercive Force(Hcb) | Intrinsic Coercive Force(Hcj) | Max. Energy Product(BH Max.) | Working Temperatures | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serial NO. | Grade | Kilogauss | Kilooersted | Kilooersted | MGOe | ℃ |
| N | N30 | 10.8-11.2 | 9.8-10.5 | ≥12 | 28-30 | ≤80 |
| N33 | 11.4-11.7 | 10.3-11.0 | ≥12 | 31-33 | ≤80 | |
| N35 | 11.7-12.1 | 11.0-11.3 | ≥12 | 33-35 | ≤80 | |
| N38 | 12.2-12.6 | 11.0-11.6 | ≥12 | 36-38 | ≤80 | |
| N40 | 12.6-12.9 | 11.0-11.6 | ≥12 | 38-40 | ≤80 | |
| N42 | 13.0-13.3 | 11.0-11.6 | ≥12 | 40-42 | ≤80 | |
| N45 | 13.3-13.7 | 11.0-11.6 | ≥12 | 43-45 | ≤80 | |
| N48 | 13.6-14.2 | 11.0-11.6 | ≥12 | 45-48 | ≤80 | |
| N50 | 14.1-14.5 | 10.4-11.4 | ≥11 | 48-50 | ≤70 | |
| N52 | 14.4-14.8 | 10.4-11.4 | ≥11 | 49.5-52 | ≤70 | |
| M | N35M | 11.7-12.1 | 11.2-11.5 | ≥14 | 33-35 | ≤100 |
| N38M | 12.2-12.6 | 11.4-11.7 | ≥14 | 36-38 | ≤100 | |
| N40M | 12.6-12.9 | 11.4-11.9 | ≥14 | 38-40 | ≤100 | |
| N42M | 13.0-13.3 | 11.4-11.9 | ≥14 | 40-42 | ≤100 | |
| N45M | 13.3-13.7 | 11.4-12.0 | ≥14 | 42-45 | ≤100 | |
| N48M | 13.6-14.2 | 11.4-12.0 | ≥14 | 45-48 | ≤100 | |
| N50M | 14.1-14.5 | 11.4-12.2 | ≥14 | 48-50 | ≤100 | |
| H | N33H | 11.4-11.7 | 10.3-11.0 | ≥17 | 31-33 | ≤120 |
| N35H | 11.7-12.1 | 10.8-11.4 | ≥17 | 33-35 | ≤120 | |
| N38H | 12.2-12.6 | 11.4-11.9 | ≥17 | 36-38 | ≤120 | |
| N40H | 12.6-12.9 | 11.4-11.9 | ≥17 | 38-40 | ≤120 | |
| N42H | 13.0-13.3 | 11.4-11.9 | ≥17 | 40-42 | ≤120 | |
| N45H | 13.3-13.7 | 11.4-11.9 | ≥17 | 43-45 | ≤120 | |
| N48H | 13.6-14.2 | 11.4-12.2 | ≥16 | 45-48 | ≤110 | |
| SH | N30SH | 10.8-11.2 | 10.1-10.6 | ≥20 | 28-30 | ≤150 |
| N33SH | 11.4-11.7 | 10.3-11.0 | ≥20 | 31-33 | ≤150 | |
| N35SH | 11.7-12.1 | 10.8-11.4 | ≥20 | 33-35 | ≤150 | |
| N38SH | 12.2-12.6 | 11.4-11.9 | ≥20 | 36-38 | ≤150 | |
| N40SH | 12.6-12.9 | 11.4-11.9 | ≥20 | 38-40 | ≤150 | |
| N42SH | 13.0-13.3 | 11.4-11.9 | ≥20 | 40-42 | ≤150 | |
| N45SH | 13.3-13.7 | 11.4-11.9 | ≥19 | 43-45 | ≤140 | |
| UH | N28UH | 10.4-10.8 | 9.8-10.2 | ≥25 | 26-28 | ≤180 |
| N30UH | 10.8-11.2 | 10.1-10.6 | ≥25 | 28-30 | ≤180 | |
| N33UH | 11.4-11.7 | 10.3-11.0 | ≥25 | 31-33 | ≤180 | |
| N35UH | 11.7-12.1 | 10.8-11.4 | ≥25 | 33-35 | ≤180 | |
| N38UH | 12.2-12.6 | 11.4-11.9 | ≥25 | 36-38 | ≤180 | |
| N40UH | 12.6-12.9 | 11.4-11.9 | ≥25 | 38-40 | ≤180 | |
| EH | N28EH | 10.4-10.8 | 9.8-10.2 | ≥30 | 26-28 | ≤200 |
| N30EH | 10.8-11.2 | 10.1-10.6 | ≥30 | 28-30 | ≤200 | |
| N33EH | 11.4-11.7 | 10.3-11.0 | ≥30 | 31-33 | ≤200 | |
| N35EH | 11.7-12.1 | 10.8-11.4 | ≥30 | 33-35 | ≤200 | |
| N38EH | 12.2-12.6 | 10.8-11.4 | ≥30 | 36-38 | ≤200 | |
| AH | N30AH | 10.8-11.2 | 10.1-10.6 | ≥35 | 28-30 | ≤240 |
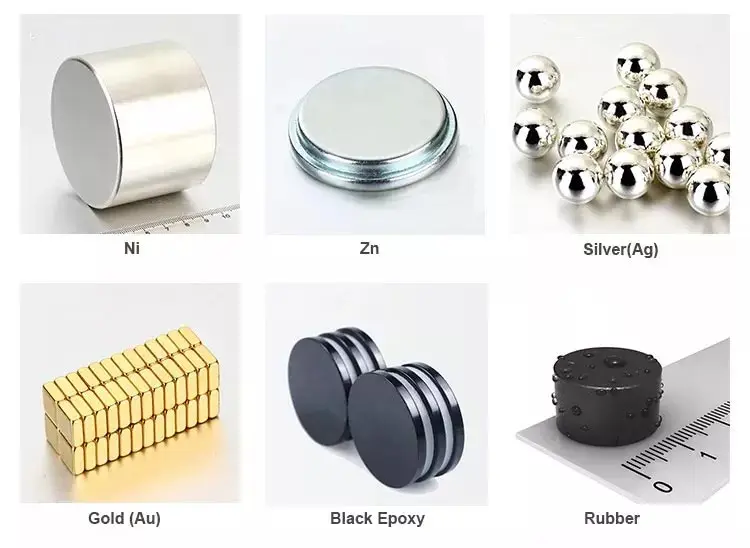
Neodymium magnet surface treatment
Neodymium magnets are powerful and widely used magnets, but neodymium magnets are inherently fragile and in most cases require careful handling and surface treatment to prevent damage and corrosion. Below are some common surface treatments for NdFeB magnets, the effectiveness of each may depend on the specific application and environment in which the magnet is used.
Electroless nickel plating. This is the most common surface treatment for neodymium magnets. It provides a protective coating that prevents corrosion and improves the durability of the magnet. Nickel plating can also improve the appearance of the magnet and make it easier to handle.
Epoxy coating. An epoxy coating can be used to provide a protective layer on the magnet. It can also help prevent chipping and cracking of the magnet’s brittle surface.
Zinc coating. The zinc coating provides a protective layer that can help prevent corrosion and improve the durability of the magnet.
Gold plating. Gold plating can be used for decorative purposes and provides a protective layer that can prevent corrosion.
Parylene coating. This is a thin, clear coating that provides a protective barrier against moisture, chemicals and other environmental factors.
| Surface | Coating | Thickness | Color | Resistance |
| (Microns) | ||||
| Passivation | 0-1 | Silver Grey | Temporary Protection | |
| Nickel | Ni+Ni | 10-20 | Bright Silver | Excellent against Humidity |
| Ni+Cu+Ni | ||||
| Zinc | Zn | 8-20 | Bright Blue | Good Against Salt Spray |
| C-Zn | Shinny Color | Excellent Against Salt Spray | ||
| Tin | Ni+Cu+Sn | 15-20 | Silver | Superior Against Humidity |
| Gold | Ni+Cu+Au | 10-20 | Gold | Superior Against Humidity |
| Copper | Ni+Cu | 10-20 | Gold | Temporary Protection |
| Epoxy | Epoxy | 15-25 | Black, Red, Grey | Excellent Against Humidity & Salt Spray |
| Ni+Cu+Epoxy | ||||
| Zn+Epoxy | ||||
| Chemical | Ni | 10-20 | Silver Grey | Excellent Against Humidity |
| Parylene | Parylene | 5-20 | Grey | Excellent Against Humidity, Salt Spray. |
| Superior Against Solvents, Gases, | ||||
| Fungi and Bacteria. |
How to Magnetize the Neodymium Magnet
Neodymium magnets are made of an alloy of neodymium, iron, and boron. To magnetize them, they must be exposed to a strong magnetic field. There are two main methods for magnetizing neodymium magnets: the first one is through a process called pulsed magnetization, and the second one is constant current magnetization
- Constant current magnetization (low-voltage large-capacity capacitor discharge), suitable for magnets with low coercive force, such as ferrite magnets, such as NdFeB magnets.
- Pulse magnetization (high voltage small capacity capacitor discharge), suitable for magnets with high coercive force, such as ferrite magnets.
Magnetization principle:
- The working principle of the constant current magnetizer: through the constant current direct current in the coil, the coil generates a constant magnetic field. Suitable for magnetizing low coercivity permanent magnet materials.
- The working principle of the pulse magnetizer: passing a momentary pulse current in the coil makes the coil generate a short super strong magnetic field. Suitable for high coercivity permanent magnet materials or complex multi-pole magnetization occasions. Widely used in permanent magnet material production and application enterprises, suitable for magnetization of various permanent magnet material parts and components, such as: alnico series, ferrite series, rare earth permanent magnet series, etc., with high efficiency and reliability. The equipment has no special requirements on the power configuration of the workplace, and it is convenient and flexible to use.


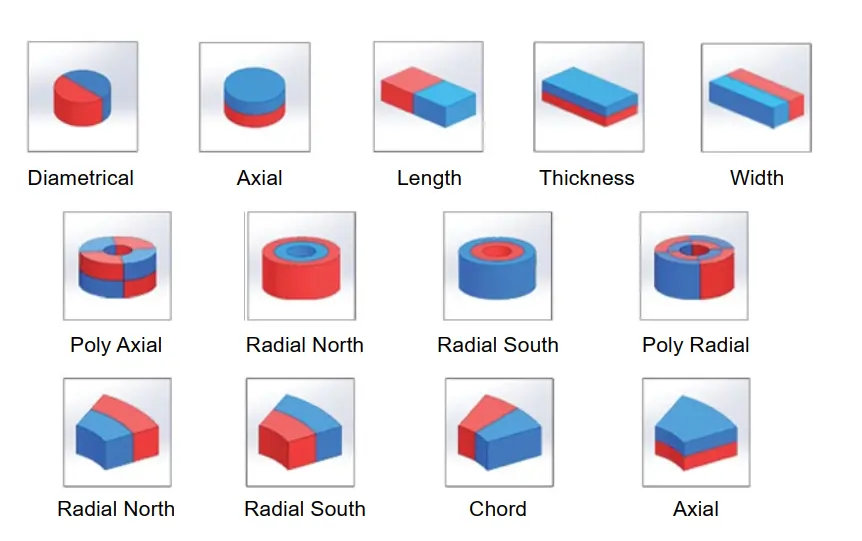
Neodymium magnet magnetization direction
Neodymium magnets are generally magnetized in the direction of thickness magnetization, axial magnetization, radial magnetization, multi-pole magnetization, radial magnetization and custom magnetization, depending on your product requirements.
- Disc, cylinder and Ring shape magnet can be magnetized Axially or Diametrically.
- Rectangle shape magnets can be magnetized through Thickness, Length or Width.
- Arc shape magnets can be magnetized Diametrically, through Width or Thickness.
- Special direction of magnetization can be customized as required.
Neodymium magnet temperature
The Curie temperature of common magnets is about 450°C for ferrite, 320-380°C for NdFeB magnets, and 860-900°C for AlNiCo.
- For the working temperature below 80°, N33-N52 performance grades can be selected
- For the working temperature between 80°–100°, N30M-N50M performance grades can be selected
- For the working temperature between 100°–120°, N33H-N48H performance grades can be selected
- For the working temperature between 120°–150°, N33SH-N48SH performance grades can be selected
- For the working temperature between 150°–180°, you can choose the performance grade of N25UH-N38UH.
- For the working temperature between 180°–200°, you can choose the performance grade of N30EH-N35UH.
- At 200 For the working temperature between °–230°, you can choose the performance grade of N28AH-N30AH.
- For the working temperature between 150°–180°, you can choose the performance grade of N25UH-N38UH
How Neodymium Magnets Are Made?
There are many manufacturing processes for magnets, the most commonly used method is called powder metallurgy, and sintered neodymium magnets are made by vacuum heating rare earth metal particles in a furnace.
Elements (mainly neodymium, iron and boron) are selected to produce the specified grade of magnet.
The chemical composition of the magnet is adjusted to determine the magnetic polarization, Curie point, magnetic flux density, and coercive force.
Process Steps of Neodymium Magnet:
Weighing → Melting & Strip Casting → Hydrogen Decrepitation → Jet Milling → Pressing → Sintering → Maching → Surface Treatment → Magnetization → Packing & Shipping
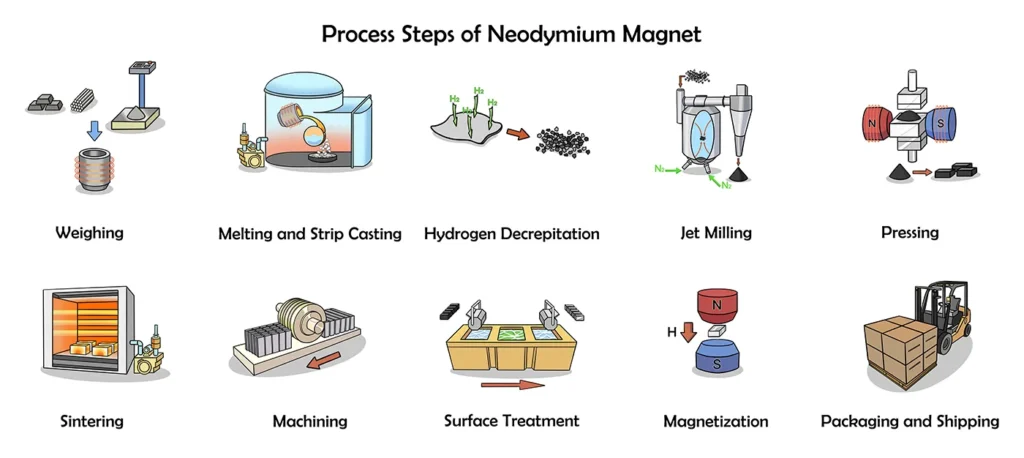
The ingredients are the basis, and the sintering and tempering is the key.
NdFeB magnet production tools: melting furnace, jaw crusher, ball mill, jet mill, compression molding machine, vacuum packaging machine, isostatic pressing machine, sintering furnace, heat treatment vacuum furnace.
What is the difference between neodymium magnets and ordinary magnets?
Neodymium magnets, also known as rare earth magnets, are permanent magnets made from an alloy of neodymium, iron and boron. They are the strongest type of permanent magnets available and are capable of producing very high magnetic fields.
Regular ordinary magnets, also known as ceramic magnets, are made from a composite of iron oxide and barium/strontium carbonate. They have less power and lower magnetic field strength than neodymium magnets.
The main difference between neodymium magnets and ordinary magnets is their strength.
NdFeB magnets have good resistance: ordinary magnets will continue to demagnetize and demagnetize in the air.
Powerful magnets are mainly made of rare elements, which have high coercive force. Under natural environment and normal conditions, their magnetic force cannot be affected at all, which ensures the stability of magnetic force. Different from the exposed magnets, the electroplating on the surface of NdFeB powerful magnets can well ensure that the magnets are not corroded by substances such as acid and alkali.
NdFeB magnets have good temperature resistance: the limit temperature and Curie temperature of powerful magnets are stronger than ordinary magnets.
No matter what kind of powerful magnets are used, the materials used are superior to magnets, so the limit temperature that the magnet itself can withstand is greatly increased, and the machine can be guaranteed to operate at the temperature used by the machine.

The hardness of NdFeB magnets is hard: the density of rare elements is added to the powerful magnets, which makes the magnets much harder than ordinary magnets. Unavoidable collisions during use will not affect the integrity of the magnet. However, ordinary magnets are fragile and cannot maintain their appearance for a long time.
Fine precision: The fineness of the powerful magnet is good. Whether it is the tolerance of the size or the value of the magnetic force of the performance, there are professional machines such as a Gauss meter to measure it, indicating the direction of magnetization, so that the error can be ignored, and the production process of ordinary magnet products is rough. For Other errors are not calculated at all, greatly reducing the already usable functionality.
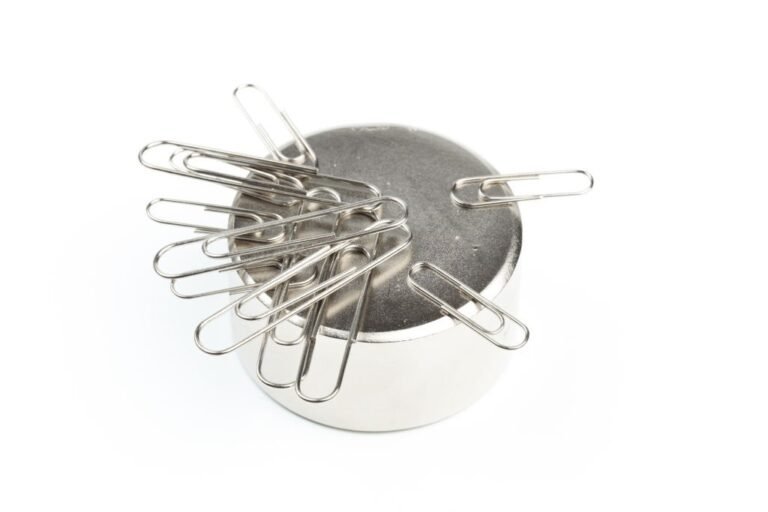

What are neodymium magnets used for
Neodymium magnets have replaced other types of magnets in modern products that require powerful permanent magnets due to their superior magnetic properties that can be used in different industries in a much smaller size. The range of applications for NdFeB magnets is as follows
Electro-acoustic field
Electronic products
Motor field
Mechanical equipment
Medical & health
Aastronomy fields
Military field
Other industries
Where to Buy Neodymium Magnets
When purchasing neodymium magnets, you can consider purchasing from neodymium magnet manufacturers, distributors and online stores. Different channels have different advantages and disadvantages, as follows:
Neodymium Magnets Manufacturer
There are many manufacturers of neodymium magnets across the globe, and they usually sell their products to customers either directly or through distributors. Some of the top manufacturers include GP Magnets, Shanghai CJ Magnet Industry, and Hangzhou YangYi Magnetics Co. Ltd.
Advantages:
Directly buying from manufacturers ensures that the magnets are authentic and of high quality.
The prices are often lower compared to dealers or online stores.
They have more control over the manufacturing process and can ensure that the magnets meet specific requirements.
Disadvantages:
There may be a minimum order quantity, which can be a problem for smaller businesses or individuals who only need a few magnets.
There may be a longer lead time for orders, especially for custom magnets.

Neodymium Magnets Distributors
Distributors are another option for purchasing neodymium magnets. They usually carry an assortment of magnets and are good for small quantities, but may be slightly more expensive. Some popular distributors include Dura Magnetics, MagnetShop.com, and Applied Magnets.
Advantages:
Dealers often offer a wide variety of magnets in different shapes and sizes, making it easier to find the right magnet for specific applications.
They can provide technical support and guidance on the use of magnets.
Dealers often have lower minimum order quantities compared to manufacturers.
Disadvantages:
Prices may be higher compared to manufacturers or online stores.
The quality of magnets may not be guaranteed if they are sourced from multiple manufacturers.

Neodymium Magnets Online store
There are many online stores that sell neodymium magnets, including Amazon, eBay, Alibaba, etc. However, it’s important to be cautious when buying from an online store and make sure the seller is reputable and the product is of high quality.
Advantages:
Online stores offer convenience and accessibility, allowing customers to shop from anywhere at any time.
Prices are often competitive, with discounts and promotions offered regularly.
There is a wide variety of options available, with many sellers specializing in neodymium magnets.
Disadvantages:
The quality of magnets may be questionable, especially from sellers who do not provide sufficient information about the manufacturing process or quality control measures.
Shipping times and costs can vary, with some sellers offering faster shipping at higher costs.

Why GP Magnets
Good Power Magnetic Products Limited is proud to be one of the largest suppliers of magnetic products in China. Our incredibly wide range allows for the selection of magnets of various sizes, strengths, shapes and functions. Our small magnets allow for precise applications, often used in manufacturing processes and integrated into mechanical objects and tools. Depending on the strength of the magnets, they can be used in different ways.
- 2D and 3D magnetic modeling of designs
- Rapid prototyping of designs
- Ability to manufacture any number of magnets
- Extensive product quality checks
- On-time delivery

Good Power Magnetic Products Limited
At GP Magnets, we design custom magnets to meet your specific needs. We combine ingenuity, deep expertise and a line of specialized equipment in order to provide you with the exact product you need, without sacrificing quality design and engineering.









